Technology
Maverick Synfuels > Technology
Maverick Synfuels develops and commercializes advanced thermo-chemical technology that converts low-value and renewable feedstocks into high-value fuels and chemicals. Our processes are feedstock flexible and can convert methane (natural gas, landfill gas, anaerobic digester gas), as well as biomass, municipal solid waste (MSW) and industrial waste, into transportable intermediates. These intermediates serve as building blocks for multiple products that readily integrate into the existing market infrastructure.
Patented Olefinity™ Process
With our patented Olefinity™ process, olefins are produced directly using a catalytic reaction known as Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis or indirectly using a Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) synthesis process.
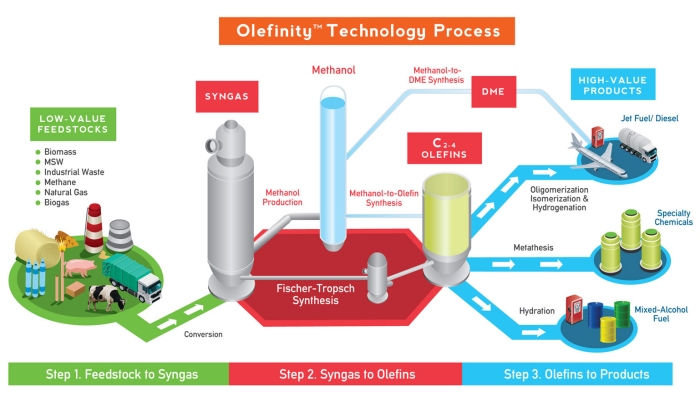
Syngas-to-Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) Process
The methanol-to-olefins (“MTO”) process is well-understood, and uses catalysts which are commercially-available. This process is more cost-effective when performed at a relatively small scale, so it is more cost-effective to produce methanol where the feedstock is located, and ship the methanol to a central hub for conversion to olefins. Once the methanol is converted to olefins, the olefins can be converted to final products.
Syngas-to-Olefins (FT) Process
Our Olefinity™ process involves three well-understood thermochemical and chemical processes that have not been previously combined into a single process. Each of the major steps is commercially available and currently used to produce other commodities.
Both of these process are illustrated below:
Step 1. Syngas Production: Feedstock is converted into a gas (synthesis gas or “syngas”) at elevated temperature.
Step 2. Olefin Production: The syngas is converted to olefins using a catalytic reaction known as Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, or, alternatively, to methanol, which is then converted to olefins using a methanol-to-olefins process.
Step 3. Olefin Conversion: The olefins are then converted into high-value products.
See Conversion Process Details for more information.